Distribution
|
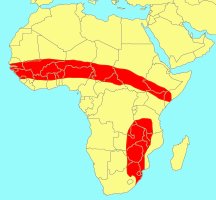
Two disjunct populations: a northern one extending from
Somali to Guinea and a southern one: NE South Africa, Zimbabwe, E Botswana, W Mozambique, Malawi,
E Zambia, SE Democratic Republic of Congo & SW Tanzania.
|
Biology
|
Pollinators:
Nigeriella fusciceps Wiebes (northern
population);
Elisabethiella comptoni Wiebes (southern population).
Non-pollinator:
Seres rotundus (van Noort).
|
Comments
|
Ficus abutilifolia
as currently defined probably constitutes two good species - one
comprising the northern population and the other the southern
population. Botanically the two populations are morphologically
distinct (Berg 1992). Gene flow is delimited both geographically and
ecologically, since each population has a
distinct species of pollinating fig wasp.
|
Habitat
|
Savanna woodland or bushveld,
usually on rocks (granite, basalt, sandstone, ironstone)
up to an altitude of 1000m. Favours hotter, low lying areas, not able to tolerate
heavy frost.
|
Frugivores
|
Birds, bats, monkeys, baboons, bushpig, warthog and
antelope such as bushbuck, nyala, duiker and klipspringer feed on the ripe figs
facilitating seed dispersal. |
Cultivation
|
Can be propogated from seeds or cuttings. Suitable species for
bonsai.
|
Etymology
|
The species name abutilifolia means "leaves like abutilon"
because of the resemblance of its leaves to those of a popular ornamental genus
Abutilon (Burrows & Burrows, 2003).
|
References
|
Berg,
C.C. 1988. New taxa and combinations in Ficus (Moraceae) in
Africa. Kew Bulletin 43: 77- 97.
Berg,
C.C. 1989. Moraceae. In: R.M. Polhill (ed.) Flora of Tropical East Africa.
A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam.
Berg,
C.C. 1990. Distribution of African taxa of Ficus (Moraccae).
[Proc. 12th AETFAT]. Mitt. inst. Allg. Bot. Hamburg 23: 401-405.
Berg, C.C. 1990. Annotated check-list of the Ficus species
of the African floristic region, with special reference and a key to the
taxa of southern Africa. Kirkia, 13: 253-291.
Berg,
C.C. 1991. Moraceae. In: E. Launert & G.Y. Pope (eds) Flora
Zambesiaca 9, 6. Natural History Museum, London.
Berg, C.C. & Hijman, M.E.E. 1989. Chapter 11. Ficus. Flora of
Tropical East Africa (ed. R.M. Polhill). 43-86. A.A. Balkema,
Rotterdam.
Berg,
C.C., Hijman, M.E.E. & Weerdenburg, J.C.A. 1984. Moracées (incl.
Cécropiacées). Flore du Gabon 26: 1–276.
Berg,
C.C., Hijman, M.E.E. & Weerdenburg, J.C.A. 1985. Moracées (incl.
Cécropiacées). Flore du Cameroun 28: 1–298.
Berg, C.C. & Wiebes, J.T. 1992. African fig trees and
fig wasps. Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen.
Amsterdam, 1-298 pp.
Bouček Z., A. Watsham & J.T. Wiebes, 1981. The fig wasp
fauna of the receptacles of Ficus thonningii (Hymenoptera,
Chalcidoidea). Tijdschrift Voor Entomologie, 124(5): 149-233.
Burrows, J. & Burrows,
S. 2003. Figs of southern & south-central Africa. Umdaus Press,
Hatfield. 379 pp.
|
Credits
|
Photographs
and distribution map © Simon van Noort (Iziko Museums of South Africa).
|
Next species
|
Ficus
bivalvata
Perrier |
|